Insect Pests of Millets: Systematics, Bionomics, and Management

4.4 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 105591 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| X-Ray for textbooks | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 191 pages |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Hardcover | : | 258 pages |
| Item Weight | : | 2.65 pounds |
| Dimensions | : | 6.14 x 0.63 x 9.21 inches |
Millets, a group of nutritious and resilient cereal crops, are staple foods for millions worldwide. However, insect pests pose significant threats to millet production, causing substantial yield losses and economic damage. This article provides a comprehensive guide to the diverse array of insect pests that infest millet crops, covering their systematics, bionomics, and effective management strategies.

Systematics of Insect Pests
Insect pests that infest millet crops belong to various taxonomic groups, primarily belonging to the Free Downloads Coleoptera (beetles),Lepidoptera (moths and butterflies),Diptera (flies),and Hemiptera (true bugs). Each taxonomic group comprises diverse families and genera, with species exhibiting unique morphological and behavioral characteristics.
- Coleoptera: Weevils, stem borers, and leaf beetles are common beetle pests of millets.
- Lepidoptera: Moths and butterflies, such as the spotted stem borer and armyworm, inflict severe damage to millet plants.
- Diptera: Midges and flies, including gall midges and shoot flies, attack millets at various stages of growth.
- Hemiptera: True bugs, such as aphids and mealybugs, feed on plant sap, weakening millet plants and transmitting diseases.
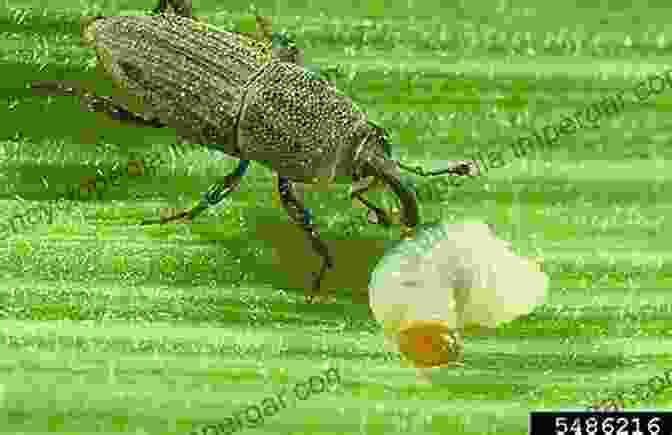

Bionomics of Insect Pests
Understanding the bionomics of insect pests is crucial for effective management. Each species has distinct life cycles, feeding habits, and environmental preferences that influence their impact on millet crops.
Life Cycles
Insect pests of millets undergo various life stages, including egg, larva, pupa, and adult. The duration and characteristics of each stage vary among species, as do the preferred host plants and feeding behaviors.
Feeding Habits
Insect pests exhibit diverse feeding habits. Some species, such as stem borers and leaf beetles, feed directly on plant tissues, causing damage to leaves, stems, and panicles. Others, like aphids and mealybugs, pierce plant tissues and suck sap, weakening plants and transmitting diseases.
Environmental Preferences
Environmental factors, such as temperature, humidity, and soil conditions, influence the distribution and abundance of insect pests. Some species thrive in warm and humid environments, while others prefer cooler and drier conditions. Understanding these preferences helps predict pest outbreaks and implement targeted management strategies.
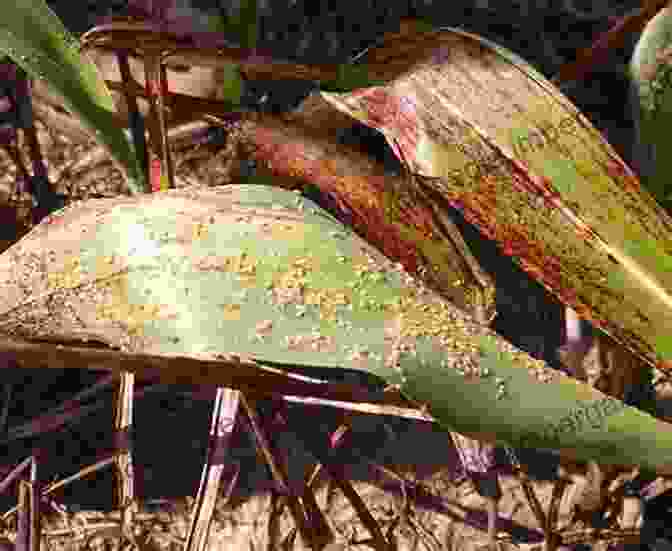
Management of Insect Pests
Managing insect pests in millet crops involves implementing a combination of preventive and control measures. Integrated pest management (IPM) approaches aim to minimize pest damage while preserving beneficial insects and the environment.
Preventive Measures
- Crop Rotation: Planting different crops in succession helps disrupt pest life cycles and reduce population buildup.
- Intercropping: Growing companion crops alongside millets can deter pests by providing physical barriers or attracting beneficial insects.
- Sanitation: Removing crop residues and managing weeds reduces pest habitats and food sources.
- Resistant Varieties: Selecting millet varieties with natural resistance to certain pests can minimize damage and yield losses.
Control Measures
- Biological Control: Introducing natural enemies, such as predatory insects or parasitoids, helps suppress pest populations.
- Chemical Control: Using insecticides as a last resort can target specific pests but should be applied judiciously to minimize environmental impacts.
- Cultural Control: Practices such as timely planting, proper irrigation, and balanced fertilization promote plant health and reduce pest susceptibility.
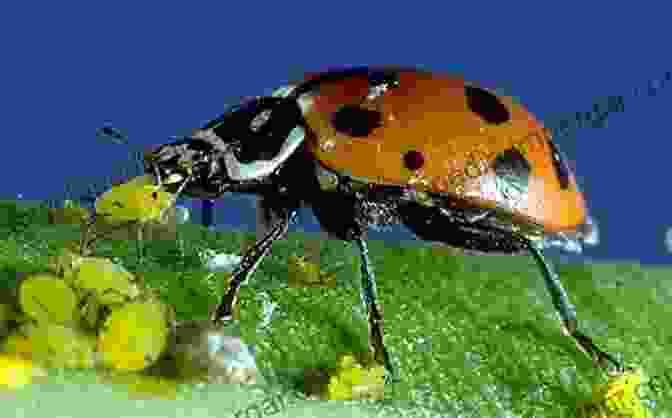

Insect pests pose significant challenges to millet production, but effective management strategies can minimize damage and ensure crop productivity. Understanding the systematics, bionomics, and management of insect pests is essential for successful millet cultivation. By implementing a holistic approach that combines preventive measures, biological control, and judicious use of chemical interventions, farmers can protect their crops and sustain millet production for future generations.
References
- Dent, D. (2000). Insect Pests of Millets. CABI Publishing.
- ICRISAT (2012). Management of Insect Pests of Millets. Patancheru, India.
- Sharma, H. C., & Jotwani, M. G. (2017). Insect Pests of Millets. CRC Press.
4.4 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 105591 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| X-Ray for textbooks | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 191 pages |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Hardcover | : | 258 pages |
| Item Weight | : | 2.65 pounds |
| Dimensions | : | 6.14 x 0.63 x 9.21 inches |
Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
 Book
Book Novel
Novel Page
Page Chapter
Chapter Text
Text Story
Story Genre
Genre Reader
Reader Library
Library Paperback
Paperback E-book
E-book Magazine
Magazine Newspaper
Newspaper Paragraph
Paragraph Sentence
Sentence Bookmark
Bookmark Shelf
Shelf Glossary
Glossary Bibliography
Bibliography Foreword
Foreword Preface
Preface Synopsis
Synopsis Annotation
Annotation Footnote
Footnote Manuscript
Manuscript Scroll
Scroll Codex
Codex Tome
Tome Bestseller
Bestseller Classics
Classics Library card
Library card Narrative
Narrative Biography
Biography Autobiography
Autobiography Memoir
Memoir Reference
Reference Encyclopedia
Encyclopedia Michael Damian
Michael Damian Clayton M Christensen
Clayton M Christensen Andrea Susan Valentine Gelfuso Goetz
Andrea Susan Valentine Gelfuso Goetz David Kruh
David Kruh Sarah Rae
Sarah Rae David Macdougall
David Macdougall Kenneth E Marshall
Kenneth E Marshall Jan Swafford
Jan Swafford Laurence W Mckeen
Laurence W Mckeen Prashanth Padmanabhan
Prashanth Padmanabhan Chuck Solomon
Chuck Solomon Chrisanna Northrup
Chrisanna Northrup Publisher S Editorial Staff
Publisher S Editorial Staff R R Palmer
R R Palmer Bj Albert
Bj Albert Jack Beatty
Jack Beatty Institute For Career Research
Institute For Career Research Dr Lafina Diamandis
Dr Lafina Diamandis Ernest Sosa
Ernest Sosa Joanne Rudling
Joanne Rudling
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!

 Yasushi InoueThe Entrepreneur's Guide to Law and Strategy: Unlocking Your Business Success
Yasushi InoueThe Entrepreneur's Guide to Law and Strategy: Unlocking Your Business Success
 Harry HayesExperience the Enthralling World of "606609 Volume Two The Self Tattooing Of...
Harry HayesExperience the Enthralling World of "606609 Volume Two The Self Tattooing Of... William ShakespeareFollow ·4.6k
William ShakespeareFollow ·4.6k Jacques BellFollow ·10.9k
Jacques BellFollow ·10.9k Dakota PowellFollow ·11.1k
Dakota PowellFollow ·11.1k Wesley ReedFollow ·12.3k
Wesley ReedFollow ·12.3k Jamal BlairFollow ·6.8k
Jamal BlairFollow ·6.8k Barry BryantFollow ·17.3k
Barry BryantFollow ·17.3k Juan RulfoFollow ·11.5k
Juan RulfoFollow ·11.5k Rex HayesFollow ·9.7k
Rex HayesFollow ·9.7k

 Terence Nelson
Terence NelsonSocial Dynamics in Systems Perspective: New Economic...
The world we live in is a complex and...

 Deacon Bell
Deacon BellUnlock the Secrets of Treasury Process Internal Controls:...
In today's competitive business...

 Finn Cox
Finn CoxThe Path Ahead: Green Energy and Technology
Embark on the...

 Rob Foster
Rob FosterThermodynamics of Surfaces and Capillary Systems: A...
Surfaces and...

 Nathan Reed
Nathan ReedUnlock the Secrets to Writing Remarkable Business School...
Embarking on the journey to business...

 David Foster Wallace
David Foster WallacePrinciples and Applications, Second Edition: Your Gateway...
In the ever-evolving realm of...
4.4 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 105591 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| X-Ray for textbooks | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 191 pages |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Hardcover | : | 258 pages |
| Item Weight | : | 2.65 pounds |
| Dimensions | : | 6.14 x 0.63 x 9.21 inches |