Malaria Immune Response: Infection and Vaccination

Malaria, a mosquito-borne disease caused by Plasmodium parasites, remains a major global health concern. The development of protective immunity against malaria is crucial for effective control and elimination strategies. This article delves into the intricate immune response to malaria infection and vaccination, exploring the key mechanisms involved and their potential implications for vaccine development.
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 2208 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 284 pages |
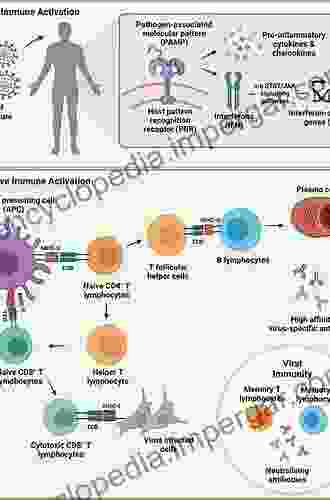
Immune Response to Malaria Infection
When a human is infected with malaria parasites, the immune system mounts a multi-faceted response to combat the infection. This response involves both innate and adaptive immunity:
Innate Immunity
Innate immunity provides a rapid but non-specific response to infection. It includes:
- Phagocytosis: Macrophages and neutrophils engulf and destroy parasites.
- Natural Killer Cells: These cells recognize and kill infected red blood cells.
- Cytokines: Chemical messengers produced by immune cells, such as interferon-gamma, activate other immune cells and trigger inflammation.
Adaptive Immunity
Adaptive immunity develops over time and provides a more specific response to infection. It involves:
- Antibodies: Produced by B cells, antibodies bind to specific proteins on the surface of parasites, neutralizing them or targeting them for destruction.
- T Cells: Helper T cells activate other immune cells, while cytotoxic T cells directly kill infected cells.
- Memory Cells: These cells remain after infection and can quickly respond to subsequent infections.
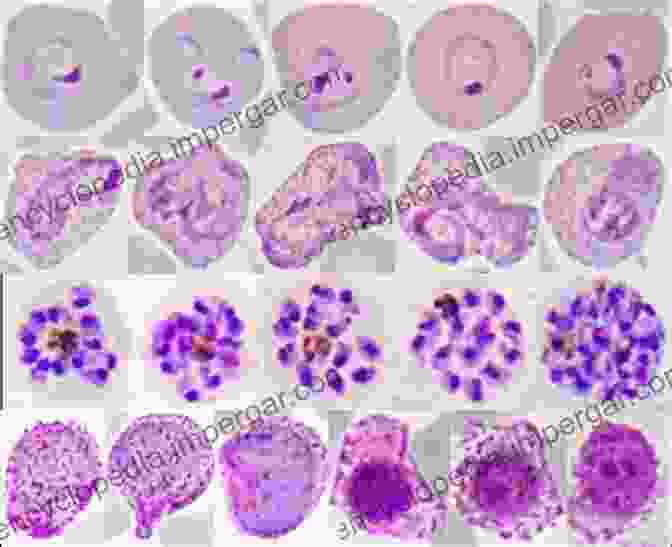
The immune response to malaria infection is complex and varies depending on factors such as the species of parasite, host genetics, and previous exposure to infection. In severe cases, the immune response can lead to excessive inflammation and organ damage.
Immune Response to Malaria Vaccination
Several malaria vaccines are currently in development or have been approved for use. These vaccines aim to stimulate the immune system to recognize and respond to malaria parasites, providing protection against infection.
Malaria vaccines generally induce antibody responses that target specific parasite proteins. Antibodies can neutralize parasites, inhibit their growth, or promote their destruction by immune cells. Some vaccines also induce T cell responses, which can enhance antibody production and kill infected cells.
The efficacy of malaria vaccines varies and can be influenced by factors such as the vaccine formulation, the target population, and the transmission intensity of malaria in the area. Currently, the only approved malaria vaccine, RTS,S (Mosquirix),provides partial protection against P. falciparum malaria in children and is recommended for use in sub-Saharan Africa.
Implications for Vaccine Development
Understanding the immune response to malaria infection and vaccination is essential for the development of more effective and durable vaccines. Key areas of research include:
- Identification of Target Antigens: Identifying parasite proteins that elicit strong and protective immune responses.
- Vaccine Adjuvants: Using substances that enhance the immune response to vaccines.
- Vector Development: Exploring novel delivery systems, such as viral vectors or nanoparticles, to improve vaccine efficacy.
- Population Immunity: Understanding how herd immunity and vaccination coverage influence the effectiveness of malaria vaccines.
- Clinical Trials: Conducting large-scale clinical trials to evaluate the safety, efficacy, and durability of malaria vaccines.
The immune response to malaria infection and vaccination is a complex and dynamic process. By understanding the key mechanisms involved, researchers and public health officials can develop more effective strategies to combat malaria. Ongoing research in vaccine development holds promise for the future, with the potential to significantly reduce the burden of this devastating disease.
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 2208 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 284 pages |
Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
 Book
Book Novel
Novel Page
Page Chapter
Chapter Text
Text Story
Story Genre
Genre Reader
Reader Library
Library Paperback
Paperback E-book
E-book Magazine
Magazine Newspaper
Newspaper Paragraph
Paragraph Sentence
Sentence Bookmark
Bookmark Shelf
Shelf Glossary
Glossary Bibliography
Bibliography Foreword
Foreword Preface
Preface Synopsis
Synopsis Annotation
Annotation Footnote
Footnote Manuscript
Manuscript Scroll
Scroll Codex
Codex Tome
Tome Bestseller
Bestseller Classics
Classics Library card
Library card Narrative
Narrative Biography
Biography Autobiography
Autobiography Memoir
Memoir Reference
Reference Encyclopedia
Encyclopedia David Fickes
David Fickes 15th Edition Kindle Edition
15th Edition Kindle Edition Alexander Von Eye
Alexander Von Eye Kelly Eden
Kelly Eden Susan D Jones
Susan D Jones Christine Gail
Christine Gail 1st Ed 2016 Edition
1st Ed 2016 Edition David Mccammon
David Mccammon Dushyant Sukhija
Dushyant Sukhija S Cameron Wright
S Cameron Wright Will Durant
Will Durant Joshua Foa Dienstag
Joshua Foa Dienstag Miriam Beloglovsky
Miriam Beloglovsky Allis Radosh
Allis Radosh Timothy Melley
Timothy Melley Jason Tetro
Jason Tetro Kevan Harris
Kevan Harris Cheryl Richardson
Cheryl Richardson William H F Altman
William H F Altman Jack Erjavec
Jack Erjavec
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!
 Leo TolstoyFollow ·8.3k
Leo TolstoyFollow ·8.3k Lord ByronFollow ·11.1k
Lord ByronFollow ·11.1k Harvey HughesFollow ·15k
Harvey HughesFollow ·15k Henry JamesFollow ·12.3k
Henry JamesFollow ·12.3k Eli BlairFollow ·13.3k
Eli BlairFollow ·13.3k Wesley ReedFollow ·12.3k
Wesley ReedFollow ·12.3k H.G. WellsFollow ·3.7k
H.G. WellsFollow ·3.7k Lucas ReedFollow ·6.3k
Lucas ReedFollow ·6.3k

 Terence Nelson
Terence NelsonSocial Dynamics in Systems Perspective: New Economic...
The world we live in is a complex and...

 Deacon Bell
Deacon BellUnlock the Secrets of Treasury Process Internal Controls:...
In today's competitive business...

 Finn Cox
Finn CoxThe Path Ahead: Green Energy and Technology
Embark on the...

 Rob Foster
Rob FosterThermodynamics of Surfaces and Capillary Systems: A...
Surfaces and...

 Nathan Reed
Nathan ReedUnlock the Secrets to Writing Remarkable Business School...
Embarking on the journey to business...

 David Foster Wallace
David Foster WallacePrinciples and Applications, Second Edition: Your Gateway...
In the ever-evolving realm of...
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 2208 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 284 pages |