Filamentous Protein Polymers: Shaping the Cytoplasmic Landscape in Bacteria and Archaea

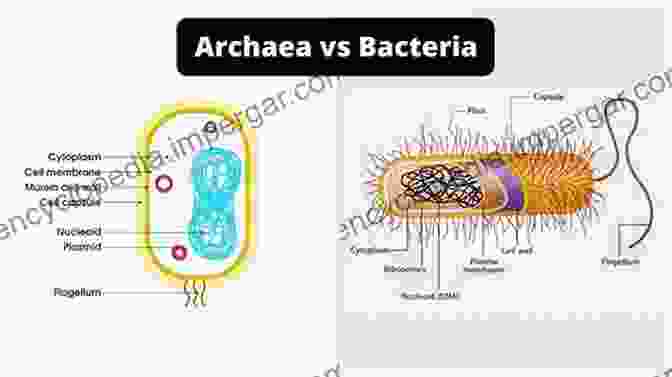
Filamentous protein polymers are essential components of the cytoplasm in bacteria and archaea, playing crucial roles in cellular organization, motility, and survival. These polymers, formed by the polymerization of specific protein subunits, exhibit remarkable structural diversity and functional versatility. This article delves into the molecular architecture, dynamics, and biological functions of these fascinating structures, providing insights into their contributions to the cellular machinery of prokaryotes.
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 9945 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 470 pages |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
Structural Diversity of Filamentous Protein Polymers
Filamentous protein polymers in bacteria and archaea exhibit a wide range of structural features. Some of the most well-studied examples include:
- FtsZ: A dynamic polymer that forms the cytokinetic ring, responsible for cell division in both bacteria and archaea.
- MreB: A helical polymer that shapes the cell wall and maintains cell shape in bacteria.
- ParM: A segregation polymer that ensures the proper segregation of chromosomes during cell division in bacteria.
- Actin-like proteins (Alps): Cytoskeletal polymers that are homologous to eukaryotic actin and play essential roles in bacterial and archaeal motility.
These polymers vary in their subunit composition, polymerization dynamics, and the presence of associated proteins that modulate their function.
Molecular Architecture and Dynamics
The molecular architecture of filamentous protein polymers is crucial for their function. These polymers typically consist of a repeating arrangement of protein subunits, which can be arranged in a linear, helical, or coiled-coil conformation. The interactions between subunits determine the stability and dynamics of the polymer.
Filamentous protein polymers are highly dynamic structures, constantly undergoing assembly, disassembly, and reorganization. The dynamics of these polymers are regulated by various factors, including GTP hydrolysis, ATP binding, and interactions with accessory proteins. This dynamic behavior allows for rapid changes in cellular organization and function.
Biological Functions of Filamentous Protein Polymers
Filamentous protein polymers are involved in a diverse range of cellular functions, including:
- Cytokinesis: FtsZ polymers form the cytokinetic ring, which constricts and separates the dividing cell into two daughter cells.
- Cell Shape Determination: MreB polymers guide the synthesis and shape the cell wall, maintaining the characteristic shape of bacterial cells.
- Chromosome Segregation: ParM polymers ensure the equal distribution of chromosomes to daughter cells during cell division.
- Motility: Alps polymers drive bacterial and archaeal motility by forming dynamic structures that interact with the environment.
These functions highlight the importance of filamentous protein polymers in the basic cellular processes of prokaryotes.
Filamentous protein polymers are crucial components of the cytoplasm in bacteria and archaea, playing essential roles in maintaining cellular organization, driving motility, and ensuring survival. Their structural diversity and dynamic behavior allow for a wide range of cellular functions. Understanding the molecular architecture and dynamics of these polymers is key to comprehending the overall functioning of prokaryotic cells.
References
1. Erickson, H. P., & Szostak, J. W. (2019). Bacterial and archaeal filamentous proteins. Annual Review of Microbiology, 73, 359-384.
2. Kaduk, M., & Egelman, E. H. (2019). Structural biology of bacterial cytokinesis proteins. Current Opinion in Microbiology, 51, 56-64.
3. Garner, E. C., & Xiao, J. (2019). Bacterial actin-like proteins. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 294(24),9627-9637.
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 9945 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 470 pages |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
 Book
Book Novel
Novel Page
Page Chapter
Chapter Text
Text Story
Story Genre
Genre Reader
Reader Library
Library Paperback
Paperback E-book
E-book Magazine
Magazine Newspaper
Newspaper Paragraph
Paragraph Sentence
Sentence Bookmark
Bookmark Shelf
Shelf Glossary
Glossary Bibliography
Bibliography Foreword
Foreword Preface
Preface Synopsis
Synopsis Annotation
Annotation Footnote
Footnote Manuscript
Manuscript Scroll
Scroll Codex
Codex Tome
Tome Bestseller
Bestseller Classics
Classics Library card
Library card Narrative
Narrative Biography
Biography Autobiography
Autobiography Memoir
Memoir Reference
Reference Encyclopedia
Encyclopedia Celine Walker
Celine Walker Richard B Hetnarski
Richard B Hetnarski 1st Ed 2018 Edition Kindle Edition
1st Ed 2018 Edition Kindle Edition Ged Gillmore
Ged Gillmore Phil Helmuth
Phil Helmuth Nina Vasan
Nina Vasan Philip Warner
Philip Warner Elias B Hanna
Elias B Hanna Hoss Belyadi
Hoss Belyadi A Kalaisekar
A Kalaisekar Chuck Solomon
Chuck Solomon Leslie Anne Warden
Leslie Anne Warden Dr Lucy Foulkes
Dr Lucy Foulkes Michael Buckley
Michael Buckley Harsha Vardhan
Harsha Vardhan Ursula Buchan
Ursula Buchan Margaret Smith
Margaret Smith Todd Harris
Todd Harris Maureen Campion
Maureen Campion Jeremy Taylor
Jeremy Taylor
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!
 Maurice ParkerDiversity and Society: Unraveling the Complex Interplay of Race, Ethnicity,...
Maurice ParkerDiversity and Society: Unraveling the Complex Interplay of Race, Ethnicity,... Jack ButlerFollow ·3.7k
Jack ButlerFollow ·3.7k Kurt VonnegutFollow ·12.2k
Kurt VonnegutFollow ·12.2k Larry ReedFollow ·11.8k
Larry ReedFollow ·11.8k Camden MitchellFollow ·18.8k
Camden MitchellFollow ·18.8k Max TurnerFollow ·12.9k
Max TurnerFollow ·12.9k Anthony WellsFollow ·5k
Anthony WellsFollow ·5k Oliver FosterFollow ·8.5k
Oliver FosterFollow ·8.5k Gustavo CoxFollow ·10.3k
Gustavo CoxFollow ·10.3k

 Terence Nelson
Terence NelsonSocial Dynamics in Systems Perspective: New Economic...
The world we live in is a complex and...

 Deacon Bell
Deacon BellUnlock the Secrets of Treasury Process Internal Controls:...
In today's competitive business...

 Finn Cox
Finn CoxThe Path Ahead: Green Energy and Technology
Embark on the...

 Rob Foster
Rob FosterThermodynamics of Surfaces and Capillary Systems: A...
Surfaces and...

 Nathan Reed
Nathan ReedUnlock the Secrets to Writing Remarkable Business School...
Embarking on the journey to business...

 David Foster Wallace
David Foster WallacePrinciples and Applications, Second Edition: Your Gateway...
In the ever-evolving realm of...
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 9945 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 470 pages |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |